It is a mystery to the common man to understand how doctors can diagnose complex neurological conditions. Doctors use imaging techniques like MRIs and CT scans to get insights into the brain and spine. Also, a lists of neurological blood tests play an important part in unveiling the root causes of neurological disorders.
Therefore, neurological blood tests are windows into the body’s biochemical processes. Consequently, they help to identify infections, inflammation, autoimmune disorders, vitamin deficiencies, etc which may be behind the symptoms.
In this blog post, we’ll explore a comprehensive list of neurological blood tests,what they are, why they’re important, and what they can reveal about your neurological health.
What are Neuropathy Tests?
Broadly speaking, neuropathy tests are diagnostic procedures that are used to assess the health and function of the nerves. Moreover, they are particularly used to detect abnormalities in the peripheral nervous system. So, doctors study the results of these tests to diagnose and monitor various neurological conditions in the peripheral nervous system.
Common neuropathy tests:
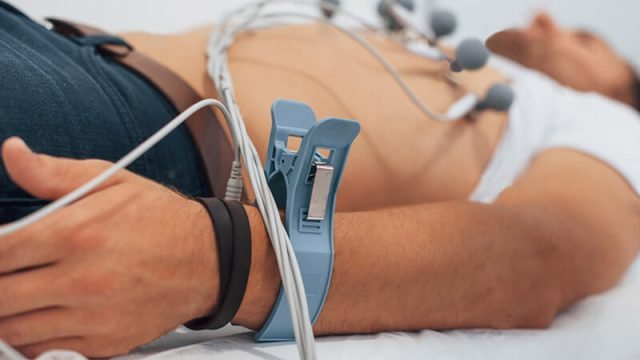
- Nerve Conduction Study (NCS): Doctors use this test to measure the speed and strength of electrical signals traveling along nerves. During the process, small electrodes are placed on the skin, and mild electrical impulses are delivered to stimulate the nerves. Consequently, the test records the speed and amplitude of the nerve’s response.
- Electromyography (EMG): With this test, doctors evaluate the electrical activity of muscles in response to nerve stimulation. During the process a thin needle electrode is inserted into the muscle. Consequently, it helps to record the muscle’s electrical activity during rest and contraction.
- Autonomic Testing: Doctors use this test to assess the function of the autonomic nervous system, which controls heart rate, blood pressure, and digestion. The process may involve measuring heart rate variability, sweat response, or blood pressure changes in response to specific stimuli.
- Quantitative Sensory Testing (QST): Doctors use this test to measure the sensitivity of the skin to light touch, vibration, heat, and cold. Therefore, it helps assess the extent of nerve damage. Moreover, it can be useful in diagnosing small fiber neuropathy.
- Skin Biopsy: During this test, a small sample of skin is removed and examined under a microscope. This helps to assess the number and health of nerve fibers in the skin. Also, this test is particularly useful in diagnosing certain types of neuropathy.
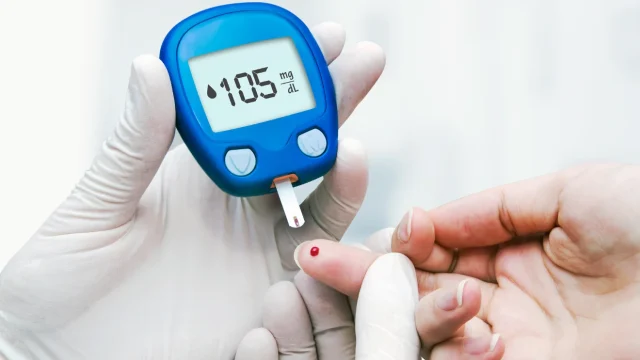
- Blood Tests: Various blood tests help identify underlying causes of neuropathy, such as diabetes, vitamin deficiencies, or autoimmune disorders.
Common Neurological Blood Tests
Neurological blood tests help in diagnosing and monitoring various neurological conditions. Also, they can help identify infections, autoimmune disorders, vitamin deficiencies, and hidden causes of neurological symptoms. Here are some common neurological blood tests:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): CBCs help to count the number of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets in the blood. Also, it helps identify anemia, infection, or inflammation, which can sometimes affect the nervous system.
- Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP): This test measures levels of electrolytes, glucose, kidney function, and liver function. Abnormalities in these areas can sometimes affect the nervous system.
- Thyroid Function Tests: It measures levels of thyroid hormones. Also, Hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can both cause neurological symptoms.
- Vitamin B12 and Folate Levels: These tests measure levels of vitamins that are important for nerve function. Also, these deficiencies can cause neurological problems.
- Tests for Metals and Minerals: These tests measure levels of metals and minerals such as lead, mercury, and copper. Exposure to these substances can damage the nervous system.
- Tests for Inflammation and Autoimmunity: These tests measure levels of inflammatory markers and antibodies that can indicate autoimmune diseases that affect the nervous system.
- Tests for Infections: These tests can identify infections that can affect the nervous system, such as Lyme disease, syphilis, or viral encephalitis.
- Tests for Blood and Bone Marrow Cancers and Pre-cancers: These tests can identify blood and bone marrow cancers that can affect the nervous system, such as leukemia or lymphoma.
- Cerebral angiogram: This helps to assess the blood vessels of the brain
However, a normal blood test does not always rule out a neurological condition. Therefore, other diagnostic tests, such as imaging studies or nerve conduction studies are needed to make a diagnosis.
Checklist of Neurological Tests
Various tests help to diagnose a nervous system disorder:
- CT scan: During CT scans a combination of X-rays and computer technology is applied to create detailed images of bones, muscles, fat, and organs. Also, CT scans are more detailed than general X-rays.
- Electroencephalogram (EEG): EEGs help to record the brain’s continuous electrical activity through electrodes attached to the scalp.
- MRI: MRIs help to make detailed images of organs and structures within the body. Also, MRI creates images with much more detail than CT scans without radiation.
- Electrodiagnostic tests, electromyography (EMG), and nerve conduction velocity (NCV): Doctors evaluate and diagnose disorders of the muscles and motor neurons with these tests. During these tests, they insert Electrodes into the muscle or place them on the skin overlying a muscle or muscle group to record electoral activity.
- Positron emission tomography (PET): Doctors take a small amount of radioactive material, a camera, and a computer to observe how well organs and tissues are working. Also, this test can see the early onset of disease.
- Arteriogram (angiogram): This helps to detect blockage or narrowing of the blood vessels.
- Spinal tap (lumbar puncture): During this test, doctors insert a special needle into the lower back into the spinal canal. Consequently, the pressure in the spinal canal and brain can be measured. Also, doctors take a small amount of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and send it for testing. Therefore, they can detect if there is an infection or other problems.
- Evoked potentials: During this test, the brain’s electrical response to visual, auditory, and sensory stimuli is recorded.
- Myelogram: During this test, a dye is injected into the spinal canal to make the structure clearly visible on X-rays. Therefore, thai test is used less commonly because MRI is widely available.
- Neurosonography: This test uses ultra-high-frequency sound waves. Consequently, the healthcare provider can analyze blood flow in cases of possible stroke. Also, this includes carotid ultrasound and transcranial Doppler.
- Ultrasound (sonography). This imaging test is used to view internal organs clearly as they function. Moreover, they also assess blood flow through various vessels.
Understanding Differential Diagnosis of Neuropathies and Its Causes
Broadly speaking, differential diagnosis of neuropathies involves considering various potential causes of nerve damage and systematically ruling them out.
Common conditions that can cause neuropathy:
Metabolic Causes:
- Diabetes: Nerves get damaged over time by high blood sugar levels leading to diabetic neuropathy.
- Vitamin Deficiencies: Nerves get impaired by Deficiencies in vitamins B12 and B6.
- Kidney Disease: There can be an accumulation of toxins in the blood, damaging nerves and leading to Kidney failure.
- Liver Disease: Liver damage can affect nerve function, particularly in conditions like alcoholic neuropathy.
Autoimmune Disorders:
- Guillain-Barré Syndrome: This is an autoimmune condition that causes rapid onset of muscle weakness and paralysis.
- Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy (CIDP) is a chronic autoimmune condition that damages the myelin sheath surrounding nerves.
Infections:
- Viral Infections: HIV and hepatitis C viruses can damage nerves.
- Bacterial Infections: Lyme disease and leprosy infections can affect nerves.
Toxic Exposures:
- Alcohol: Excessive alcohol consumption can damage nerves.
- Heavy Metals: Continuous exposure to heavy metals like lead and arsenic can cause neuropathy.
- Certain Medications: Chemotherapy drugs and certain antibiotics, can have neurotoxic effects.
Hereditary Conditions:
- Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease: These inherited disorders affect the nerves.
- Hereditary Sensory and Autonomic Neuropathies: These inherited disorders affect sensory and autonomic nerves.
Traumatic Injuries:
- Nerve Compression: Carpal tunnel syndrome that compresses nerves can cause localized neuropathy.
- Nerve Injury: Trauma or surgery may injure nerves and can cause neuropathy.
Other Causes:
- Vasculitis: Neurophathy may be due to inflammation of blood vessels that can reduce blood flow to nerves.
- Cancer: Cancers like lymphoma and multiple myeloma, can produce proteins that damage nerves.
Medications That Help Manage the symptoms of neuropathy
A combination of medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications can help manage the symptoms of neuropathy. Also, the choice of medication will depend on the underlying cause of the neuropathy and symptoms.
- Anticonvulsants: These types of medications were originally developed to treat seizures. Also, they include such as gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica), for managing neuropathic pain.
- Antidepressants: Sometimes doctors prescribe antidepressants, like tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), that can help alleviate neuropathic pain.
- Topical Medications: Sometimes, simple topical creams or patches containing lidocaine or capsaicin can provide localized pain relief.
- Pain Relievers: Doctors also suggest pain relievers like acetaminophen (Tylenol) or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may help with mild to moderate pain.
Important Considerations:
- Side Effects: It is essential to consult your doctor about the risks and benefits as all medications have potential side effects.
- Individual Response: You will discover the right medication by trial and error as people respond differently to medications.
- Regular Monitoring: You have to be monitored by your doctor to track progress and adjust your medication as needed.
Conclusion
This comprehensive blog must have enlightened you about the importance of Neurological blood tests in diagnosing and managing a wide range of neurological disorders. Also, you must have a fair idea of how these tests shed light on underlying conditions, and empower healthcare professionals to develop effective treatment plans and improve patient outcomes.
Therefore, if you’re experiencing neurological symptoms, it’s crucial to consult with a qualified neurologist. Consider visiting Apollo Clinic Ulubari which offers comprehensive neurological care, including advanced diagnostic tests and expert consultations.
Don’t put your health at risk. Book an appointment today at Apollo Clinic Ulubari.