Gestational diabetes and pregnancy health often go hand in hand. Maintaining your blood sugar levels effectively is not only for your own well-being, but also for your baby’s health, so this is a serious issue. If you have just been diagnosed with gestational diabetes, you might be thinking that you are in over your head and that this is understandable, but you are not alone, and with the correct support, it is a very controllable condition.
Pregnancy is a period of excitement, anticipation, and surprises, and with some pregnant women, their surprise diagnosis is gestational diabetes, a condition that impacts the manner in which your body metabolizes sugar during pregnancy. But do not worry because you are not alone, and with some attention and effort, you can control your gestational diabetes throughout your pregnancy.
If you have just been diagnosed, you may be thinking: What can I eat? Will my baby be alright? Do I need to give up all my favourite foods? These are all valid questions, and we can answer them. This is a stressful time, but with a little bit of planning, a little bit of support, and a little balance of nutrition, you can move forward from here in a healthy and confident manner.
If you are attempting gestational diabetes control for the very first time, or are just looking to maximize your current food habits, welcome! In the following blog, we will outline some easy meal plans, foods to eat and avoid, and practical tips that will allow you to control gestational diabetes, not only limiting diet during pregnancy but instead empowering the pregnancy.
What is Gestational Diabetes?
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is a pregnancy-related form of diabetes, most commonly occurring from the 24th to 28th week, due to hormonal shifts causing the body not to use insulin properly. Similar to Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes, gestational diabetes will, in most cases, cease after birth but needs close tracking and diligent handling to ensure peak health of both mother and infant.
In gestational diabetes, a body that might previously have been thought of as having maximally functional insulin function starts losing the capacity to respond to existing insulin (insufficient effect on lowering blood sugar). In gestational diabetes, blood glucose elevation is seen during pregnancy, which can affect other complications of pregnancy. When not controlled adequately, gestational diabetes can result in:
- Macrosomia (overweight at birth) raises the risk of injury to the baby during birth or of having a cesarean delivery.
- Premature birth and related health complications for the infant.
- Neonatal hypoglycaemia (baby’s low blood sugar after birth).
- Jaundice, respiratory distress syndrome, and other complications of the newborn.
- Increased lifetime risk of developing Type 2 diabetes for the mother and the infant.
- Preeclampsia (blood pressure elevation during pregnancy) can be harmful if left untreated.
Luckily, gestational diabetes can be well-controlled through a combination of:
- Healthy diet: Balanced eating with appropriate portion sizes and carbohydrates distributed throughout the course of a day.
- Regular physical activity: Mild to moderate exercise, such as walking or prenatal yoga, maintains blood sugar levels.
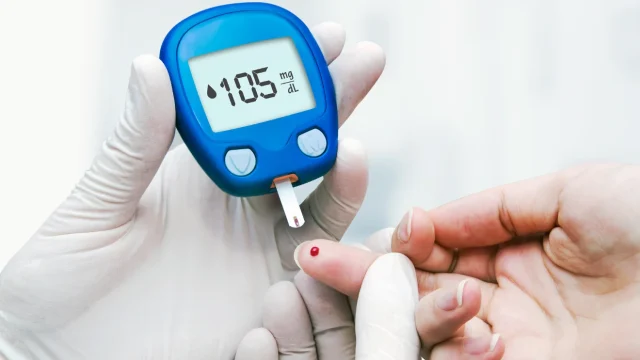
- Monitoring blood sugar: Regular testing makes sure they remain within the target range.
- Medication or insulin therapy, if necessary, according to the doctor’s advice.
After giving birth, blood glucose will typically return to normal, but it is worth it for women who had gestational diabetes to have postpartum glucose screening and routine screening in the future. Up to 50% of women with GDM may get Type 2 diabetes later in life, so maintaining a healthy lifestyle after pregnancy is crucial.
If you’re pregnant or planning to conceive, regular prenatal check-ups and early screening can help detect gestational diabetes and reduce associated risks, supporting a safe and healthy pregnancy.
Importance of Diet in Managing Gestational Diabetes
Managing gestational diabetes involves balancing a number of elements, and diet is one important component. It is possible to manage the condition effectively by consuming foods that help to control blood sugar levels. Following the right diet for a healthy pregnancy can help to keep blood sugar controlled, minimize risk factors for the baby, and maintain the mother’s energy levels.
What should you consider in order to control blood sugar through diet? Let’s examine some dietary strategies and food examples that may be suitable for women with gestational diabetes.
Essential Elements of a Gestational Diabetes Diet
In planning the diet for a healthy pregnancy, there are certain principles that have to guide your diet. Some of these principles are carbohydrate limitation, low-glycemic index foods, and increased numbers of smaller meals during the day.
1. Prioritize Complex Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates directly affect your blood sugar levels, so it’s essential to select the correct type. Replace refined sugars and white bread with whole grains and complex carbohydrates. Brown rice, whole-wheat bread, quinoa, and oats are all good options. These foods are slowly digested, keeping your blood sugar levels stable.
2. Incorporate Protein into Every Meal
Protein is necessary for the baby’s development and growth, and also to control blood sugar levels. Including a source of protein in each meal will stabilize your blood sugar and prevent spikes. Good protein sources are lean meats like chicken, turkey, fish, tofu, and eggs.
3. Select Healthy Fats
Healthy fats that include avocado, olive oil, nuts, and seeds, are required for a healthy pregnancy. The healthy fats help to develop the baby’s brain and nervous system and may even help with improved control of blood sugar.
4. Fruits and Vegetables Are Your Friends
Fruits and vegetables are packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and fibre. Yet, fruits that are low on the glycemic index, such as berries, apples, and pears, need to be eaten. Leafy greens, broccoli, and bell peppers should also be a part of your diet. These nutrient-dense foods regulate blood sugar and do not allow you to feel hungry.
5. Avoid Sugary and Processed Foods
It is advisable to steer clear of sugary foods and beverages, which can lead to quick increases in blood sugar. Processed meals, fast food, and sweetened drinks should be avoided or consumed in limited quantities. Instead, have home-cooked meals made from fresh ingredients to provide the best quality nutrition for you and your baby.
Sample Diet Plan for Gestational Diabetes
Here is a sample meal plan to help you manage your gestational diabetes:
Breakfast:
- Scrambled eggs with spinach and mushrooms
- 1-2 moong dal cheelas with grated veggies (like lauki, carrot or spinach)
- A handful of mixed berries
- 1 slice of papaya or ½ guava (low sugar and high goodness!)
Mid-Morning Snack:
- Small handful of almonds, small handful of roasted makhana or unsalted peanuts, an apple or pear
Lunch:
- 2 whole wheat phulkas (no ghee at this point!)
- 1 bowl of masoor dal or chana dal (cooked with low oil)
- 1 cup of sabzi (you can try tinda, lauki, bhindi or spinach – cooked with light spices)
- A crunchy salad: cucumber, tomato and grated carrot
- 1 bowl of plain curd (your gut will thank you)
Afternoon Snack:
- 1 cup of masala chai or herbal tea (no sugar) or 1 bowl of sprouted moong salad
Dinner:
- 1-2 chapatis or ½ bowl of brown rice
- 1 bowl of vegetable stew or paneer bhurji
- 1 bowl of sautéed methi or palak (keep it plain and simple)
- Salad or a few pieces of steamed carrot + cucumber
- Pro-tip: Try to eat dinner at least 2 hours before you sleep
Evening Snack:
- A small serving of cottage cheese or a boiled egg
Tips for Blood Sugar Control During Pregnancy
Along with following a healthy diet, you may also want to consider these other tips for managing blood sugar levels:
- Eat Smaller, But More Often: Consider eating five to six smaller meals, rather than three larger meals. This will help to prevent your blood sugar from spiking and dipping.
- Keep Active: Staying physically active is very important during pregnancy, but be sure to talk with your healthcare provider before changing or starting any new exercise routine. In general, low-impact movements like walking, swimming, or prenatal yoga can be helpful in regulating and maintaining blood sugar levels.
- Drink Water: Staying hydrated is always important and even more so during pregnancy. Drinking fluids helps your body to function properly, but it may also keep your blood sugar more steady.
- Monitor Blood Sugar: Follow your healthcare provider’s guidance. Be sure to regularly monitor your blood sugar levels. Regularly falling numbers in this area will give you a good sense of your progress, plus help you to gauge whether you need to make changes in your diet.
Foods to Avoid with Gestational Diabetes
There are certain foods that will increase your blood sugar levels and must be limited or avoided. These include:
- Refined carbohydrates (e.g. white bread, pastry, sweet cereals)
- Sweet snacks (e.g. sweets, cake, biscuits)
- Fruit juices containing added sugars (e.g. soda, normal fruit juice)
- Fried foods and processed meats
When to Seek Medical Advice
It is important to consult with your medical provider throughout your pregnancy, including making diet changes to help with blood sugar management. Appointment visits, blood sugar readings, and collaboration between you and your doctor will keep you on the path to success.
If you experience any unexplained blood sugar changes or unusual symptoms, you should contact your medical provider. They will help you with suggestions and adjustments to your treatment plan.
Conclusion
Don’t let gestational diabetes dictate your pregnancy experience. With the right support, you can learn how to manage your health and enjoy this wonderful experience. Apollo Clinic in Guwahati develops a unique care plan through 3 unique sources of expert care. The team of expert gynaecologists, diabetologists, and nutritionists will work with you to manage your blood sugar levels and protect your baby’s health.

Dr. Tanma Saikia Das

Dr. Asha Agarwal

Dr. Meghali Devi

Dr. Mithun Bhartia
With Apollo Clinic’s guidance and support, you aren’t alone as you make the transition into a safe, healthy motherhood.
Contact us today to book your appointment at +91-9085612000.