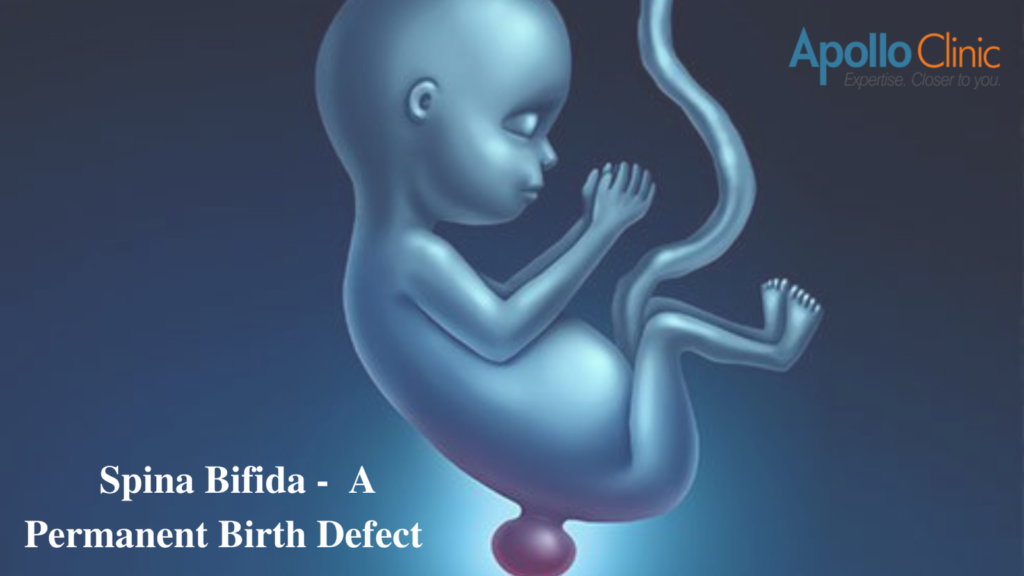
Spina Bifida – A Definition
Spina Bifida is a condition where a baby’s neural tube (a collection of cells developed into the spinal cord and brain) does not close entirely in the initial weeks of embryonic development. Therefore, bones present in the spinal column do not completely close around the spinal cord’s nerves. Thus, a part of the cord sticks out through a spinal opening. Hence, this leads to the permanent spinal cord and nerve damage. The condition is usually found along the backbone, often at the small of the back.
This usually occurs in the first twenty-eight days of a woman’s pregnancy, when the neural tube is developing. Also, the severity of the cases depends on the spinal opening’s size and location. Additionally, whether the nerves and spinal cord are affected.
What Are the Types?
As with most birth conditions, spina bifida occurs in varying degrees. Depending on the severity, they cause minor to significant health challenges:
- Spina Bifida Occulta
Spina bifida occulta is the most common and mildest form of the condition, which involves a tiny portion of the spin. It is usually asymptomatic and does not require treatment. But it can be diagnosed by purple or red colour, dimple, or a tuft of hair. As children grow, they could face weakness in the legs and the bladder system.
- Meningocele
Meningocele is less common, where the meninges (the membrane surrounding the spinal cord) protrudes through the spinal opening, which causes a lump on the back. However, surgery can treat it with minimal nerve damage due to the normal development of the cord.
-
Myelomeningocele
This is the harshest form of spina bifida, as the spinal cord does not correctly develop, and a significant part of the spinal cord protrudes through the back. A sac that contains blood vessels and cerebrospinal fluid remains uncovered, exposing the tissues and nerves.
Babies born with this condition experience hydrocephalus (spinal fluid buildup in the brain), which causes blindness, seizures, or brain damage if left untreated. They often experience weakness or even paralysis in the lower part of the body.
What are the symptoms?
Babies affected with this condition show different symptoms than the next. Still, they include a sac, hairy patch, birthmark or dimple on the lower back, leg paralysis, incontinence or constipation, lack of a spine in the sac area, and hydrocephalus. Also, bone problems, heart problems, and low intelligence are observed as well.
What is the cause?
The best neurologist doctor in Guwahati does not have an exact reason why spina bifida occurs. However, it could be a combination of environmental, nutritional, and genetic factors.
Can you detect spina bifida when you’re pregnant?
Yes, a neurology doctor in Guwahati can detect spina bifida in a fetus through an ultrasound (sonogram), checking for alpha-fetoprotein in a blood test, and protein levels in an amniocentesis.
Is spina bifida treatable and preventable?
Though we do not have a cure for it, medication, surgery, and physical well as behavioral therapy help manage the condition. With the correct medical treatment and emotional support, children born with it lead whole and productive lives.
If you are pregnant or plan to have a baby, take folic acid supplements after discussing them with your doctor. Upgrade yourself to dietary supplements, vitamins, and OTCC drugs. Take special care if you are obese or diabetic, do not overheat your body, and treat fevers with medicine immediately.
At Apollo Clinic Guwahati, we offer the highest standards of medical care for babies born with spina bifida. Please reach out to us for expert advice, guidance, and treatment at Apollo Guwahati.